Your help helps us to inform the story
From reproductive rights to local weather change to Massive Tech, The Unbiased is on the bottom when the story is growing. Whether or not it is investigating the financials of Elon Musk’s pro-Trump PAC or producing our newest documentary, ‘The A Phrase’, which shines a light-weight on the American ladies preventing for reproductive rights, we all know how essential it’s to parse out the info from the messaging.
At such a crucial second in US historical past, we want reporters on the bottom. Your donation permits us to maintain sending journalists to talk to either side of the story.
The Unbiased is trusted by Individuals throughout your entire political spectrum. And in contrast to many different high quality information shops, we select to not lock Individuals out of our reporting and evaluation with paywalls. We consider high quality journalism needs to be out there to everybody, paid for by those that can afford it.
Your help makes all of the distinction.
Shut
Learn extra
Practically all the Arctic’s sea ice might soften by the summer time of 2027, a gaggle of worldwide scientists has warned.
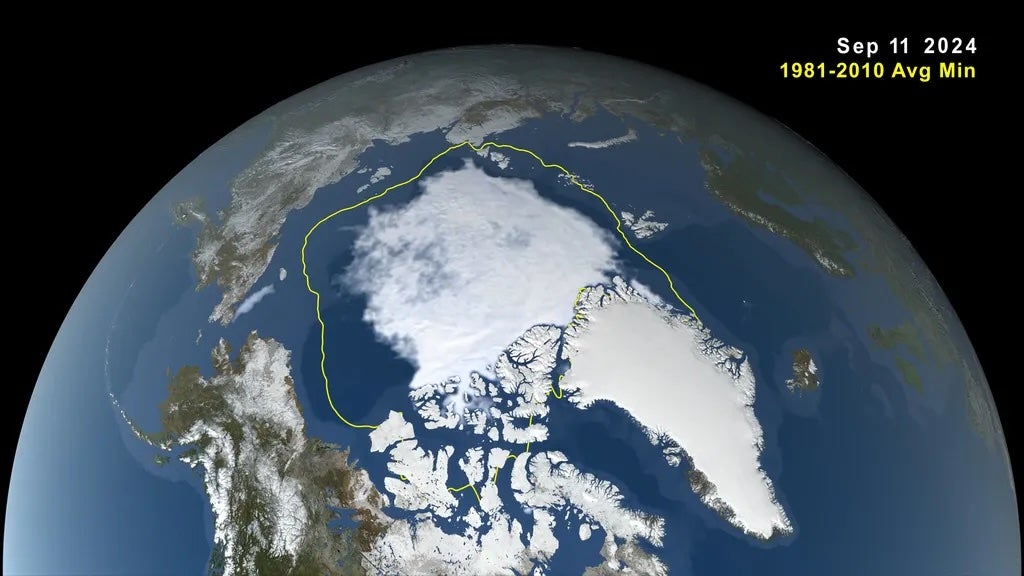
Sea ice – frozen seawater that floats on the ocean’s floor – within the area has diminished to near-historic lows following many years of shrinking and thinning in one of many fastest-warming areas on the planet. The warming has been pushed by ever-increasing greenhouse gasoline emissions: the results of humanity’s reliance on fossil fuels. The day when nearly all of the ice disappears is drastically regarding to researchers, who aren’t but certain what repercussions it may need.
Analysis revealed Tuesday within the journal Nature Communications finds the Arctic shall be “ice-free” when it has lower than 1 million sq. kilometers of ice. The least quantity of sea ice, which generally melts and reforms with the altering of the seasons, in a day this yr was at 1.65 million sq. miles: a stark decline in comparison with the common between 1979 and 1992.
“The local weather fashions present that until we will keep beneath 1.5 levels Celsius globally within the climatological common, which is changing into much less and fewer probably each month mainly, it’s assured that we are going to see ice-free situations this century,” Alexandra Jahn, an affiliate professor of atmospheric and oceanic sciences on the College of Colorado Boulder and co-author of the analysis, instructed The Unbiased on Monday.
Nations agreed in 2015 to restrict international warming to 1.5 levels Celsius of warming. However, the United Nations stated in October that Earth is on the monitor for as a lot as 3.1 levels – and that this might be “catastrophic.”
open picture in gallery
The Arctic has already misplaced about half of its sea ice, in comparison with the Eighties on the finish of the summer time. It’s recognized that extra warming has delayed ice formation, and resulted in thinner sea ice progress. The ice is less complicated to soften and extra of it melts in greater temperatures within the spring. And, a excessive stress system over the Central Arctic has been noticed protecting heat air there. When the ice is skinny, extra storms type within the spring and summer time that may break up the ice and additional speed up ice soften. These items occur for a number of years in a row, main to an enormous discount in Arctic sea ice.
Fashions undertaking that storms and warmth waves will proceed to extend sooner or later, because the local weather continues to heat.
“Emissions are nonetheless rising, we’re having document heat years yr after yr, and in order that’s simply all resulting in adjustments in all facets of the local weather system…” Jahn stated.
It’s due to these adjustments, and in a “excellent storm,” that an ice-free day might occur “ahead of most individuals anticipate.”
However, it will likely be “some of the clear adjustments within the pure setting resulting from anthropogenic-driven local weather change,” she famous.
“After we attain ice-free situations then nearly all of the Arctic Ocean, 94 % of it, can have no ice anymore. So, we’re going from a white Arctic ocean to a blue Arctic ocean. And so, visually that’s a extremely massive change and actually illustrates how a lot anthropogenic greenhouse gases can change the pure setting,” Jahn defined.
Primarily based on satellite tv for pc knowledge from the Nationwide Snow and Ice Knowledge Middle, researchers are sure that the Arctic will lose extra ice. Most fashions predicted that the primary ice-free day might occur inside 9 to twenty years after 2023, no matter how people alter their greenhouse gasoline emissions.
“As we method an ice-free Arctic, there’s a large number of impacts on the local weather system and on the ecosystem, in addition to on the folks dwelling within the Arctic. On how they will use the ocean ice for transportation and searching and issues like that,” Jahn stated.
open picture in gallery
However, whether or not or not it occurs, stays up within the air. There’s uncertainty in projections based mostly on local weather fashions. So, it might occur between three years and 50 years.
“These projections are probabilistic, so we’re not saying an ice-free Arctic will occur in three to 6 years. It’s actually three to 50 years. That’s what the fashions are displaying, relying on the variability and the energy of the worldwide emissions … However, it might occur sooner than folks would possibly anticipate …” she stated.
To keep away from an ice-free day, the world should restrict international warming, researchers warn. There may be nonetheless a risk that, if the world urgently acts, ice-free situations could not ever come about, they are saying.
“So, below the bottom emissions situation there are a number of fashions that don’t have an ice-free day earlier than the top of the century. However, a number of additionally do. If we will keep there, then it’s form of as much as probability whether or not we get a speedy ice-loss occasion some years the place we get to ice-free situations, anyway,” stated Jahn.
“Whereas, if we go above 1.5 levels, we’re mainly assured to see ice-free situations. So, decreasing greenhouse gasoline emissions by any quantity will have an effect on how a lot ice stays within the Arctic Ocean.”





















